What’s Linux?
Linux is a free and open-source operating system kernel. Linux is part of a family of operating systems that bundle various pieces of software to form a complete OS, called Linux distros.
What’s Cybersecurity?
It is the practice of protecting important information from digital threats.
That important information can be anything but ranges from systems, networks, and personal data.
How much information do you store online?
Why Care?
Cybersecurity offers diverse career paths for those who are maybe looking for something a little different.
As technology evolves more and more, so does the need for security. Which means... increased job opportunities.
Some real life examples...
During the PS3’s run, hackers attacked Sony’s Playstation Network (successfully!). This resulted in names, emails, passwords, and credit card information all being exposed.
PSN was then shut down for about a month, meaning no one could play online.
Speculated hacker groups were famously Anonymous or LulzSec but Sony never publicly identified.
Cost Sony over 171 million dollars
Some real life examples...
Just last year, Lurie’s Children Hospital here in Chicago experienced a cyberattack. Sensitive information like: names, addresses, Social Security Numbers, medical records, etc. all got exposed.
It’s approximated over 791,784 patients had their data exposed.
To fight against breach, the hospital had to shut down their online system. Resulted in significant delays and inconveniences for sick children.
Rhysida Ransomware claims they sold the data for 3.4 million dollars

Linux and Cybersecurity
Linux serves as a foundation and is an essential for many security-related tools.
Linux being open-source makes it more secure and customizable than Windows or macOS
Linux is more resistant to Malware than both Windows and macOS.
Open your terminal!
Connecting to a Server
Terminal
This is what your computer understands!
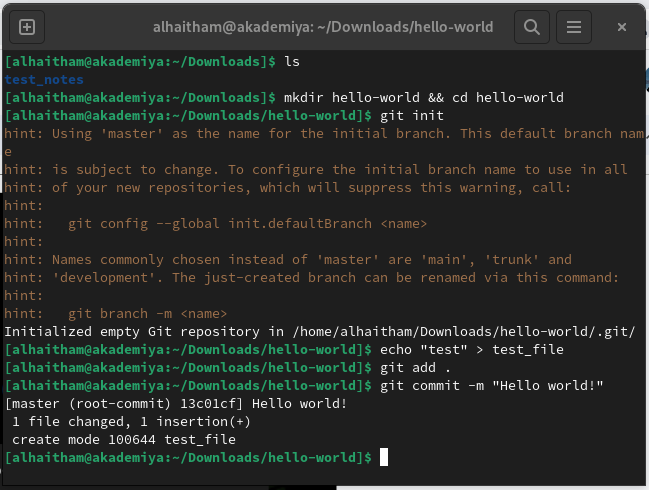
Connecting to a Server
How to get to the terminal?
| Windows | Open
Windows Powershell |
|---|---|
| macOS and Linux | Open Terminal |
| iOS | Install Terminus |
| Android | Install Termux and |
sudo apt install openssh-client |
ssh
OpenSSH SSH client (remote login program)
SSH
Syntax
ssh <username>@<server>
Example
batman@laptop:~$ ssh batman@batcomputer
Password for batman@batcomputer:
Last login: Sun Jan 20 18:21:53 2019 from 131.225.225.255
batman@batcomputer ~$Connecting to the Lab Server
Hostname
The server’s hostname is malware.cs.uic.edu
Syntax
ssh user<XX>@malware.cs.uic.edu
Where <XX> is a random number.
The password is uninstallwindows.
Example
batman@laptop:~$ ssh user1@malware.cs.uic.edu
Password for user1@lug-boat:
Last login: Sun Jan 20 18:21:53 2019 from 131.129.46.66
user1@lug-boat ~$Intro to Coreutils
What are coreutils?
Common Examples




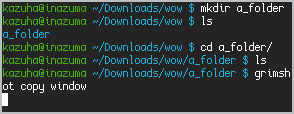
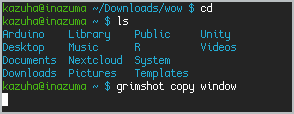
Structure of a Linux Command
Format
{command} {options/flags} {arguments}
Example
rm -r oldStuff
| Command | rm |
|---|---|
| Flags | -r |
| Arguments | oldStuff |
Command Overview
ls
cd
mkdir
rm
pwd
mv
cp
cat
I Need Help!
Use man!
Accesses reference manuals for all commands on your system.
batman@batcomputer:~$ man cat
CAT(1) User Commands CAT(1)
NAME
cat - concatenate files and print on the standard output
SYNOPSIS
cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
DESCRIPTION
Concatenate FILE(s) to standard output.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
...Permissions In Linux, all files are owned by a user and a group.
ls output
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ ls -al
total 31496
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 98 Sep 30 00:20 .
drwx------ 1 aether aether 882 Feb 17 02:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 26131919 Aug 17 2024 addressing_your_concerns.mp4
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 0 Sep 30 00:20 Screencasts
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.movPermissions can be listed with ls -al.
Permissions Permissions are important because they safegard unauthorized users from accessing data.
-rw-r–r– 1 aether aether 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.mov
What does this mean?
Users and Groups What are users and groups? A user is the account that you are logged into on a Linux machine.
Who am I? Use whoami and who!
aether@teyvat ~ $ whoami
aether
aether@teyvat ~ $ who
aether tty1 2025-02-16 00:40
aether@teyvat ~ $Permissions We can change permissions of a file or directory
with chmod.
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ ls -al
total 31496
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 98 Sep 30 00:20 .
drwx------ 1 aether aether 882 Feb 17 02:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 26131919 Aug 17 2024 addressing_your_concerns.mp4
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 0 Sep 30 00:20 Screencasts
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.mov
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ chmod 600 vibe_2.mov
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ ls -al
total 31496
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 98 Sep 30 00:20 .
drwx------ 1 aether aether 882 Feb 17 02:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 26131919 Aug 17 2024 addressing_your_concerns.mp4
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 0 Sep 30 00:20 Screencasts
-rw------- 1 aether aether 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.movPermissions We can also change who owns a file with
chown.
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ ls -al
total 31496
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 98 Sep 30 00:20 .
drwx------ 1 aether aether 882 Feb 17 02:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 26131919 Aug 17 2024 addressing_your_concerns.mp4
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 0 Sep 30 00:20 Screencasts
-rw------- 1 aether aether 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.mov
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ chown root:root vibe_2.mov
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ ls -al
total 31496
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 98 Sep 30 00:20 .
drwx------ 1 aether aether 882 Feb 17 02:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 aether aether 26131919 Aug 17 2024 addressing_your_concerns.mp4
drwxr-xr-x 1 aether aether 0 Sep 30 00:20 Screencasts
-rw------- 1 root root 6115622 Mar 25 2024 vibe_2.movTry this!
Elevating Permissions This didn’t work because only the
root user1 can change ownership to
root.
I cheated...
sudo You can elevate to root permissions using
sudo!
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ chown root:root vibe_2.mov
chown: changing ownership of 'vibe_2.mov': Operation not permitted
aether@teyvat ~/Videos $ sudo !!
sudo chown root:root vibe_2.mov
[sudo] password for aether:Logs How is my system doing?
You can view logs in /var/log, which is a folder
containing all logs.
/var/log
aether@teyvat /var/log $ ls -al
total 4480
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 240 Feb 16 00:39 .
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 116 Feb 16 00:39 ..
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Mar 21 2024 audit
-rw-rw---- 1 root utmp 6528 Feb 3 20:36 btmp
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 38 Mar 21 2024 cups
drwx--x--x 1 root gdm 0 Mar 21 2024 gdm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1589311 Jan 30 11:20 haskell-register.log
drwxr-sr-x+ 1 root systemd-journal 76 Mar 21 2024 journal
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root utmp 292292 Feb 6 18:17 lastlog
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Jan 19 2024 old
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2219671 Feb 17 00:32 pacman.log
drwxr-xr-x 1 passim passim 18 Jun 28 2024 passim
drwx------ 1 root root 0 Mar 21 2024 private
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 39 Dec 21 04:28 README -> ../../usr/share/doc/systemd/README.logs
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root utmp 529152 Feb 16 00:40 wtmp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 64141 Feb 17 00:01 Xorg.0.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 106890 Feb 16 00:39 Xorg.0.log.old
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 43467 Oct 23 09:33 Xorg.2.logBinary Logs Some logs aren’t in /var/log, some are
managed by systemd2.
For example, to view the users who have logged in via
ssh...
ssh Use journalctl!
sudo journalctl -u ssh
Networking Most of the main attack vectors on a Linux machine are through the network.
You can view all the current connections on the operating system
using netstat.
Netstat
ewong25@lug-boat:~$ sudo netstat | tail -n 20
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 237928
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 22879
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 246821
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 239928
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 237927
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 19958
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 20252 /run/systemd/journal/stdout
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 14954
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 239629 /run/systemd/journal/stdout
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 234299
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 234172 /run/dbus/system_bus_socket
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 20834
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 240729
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 203781
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 237887
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 236820
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 23376 /run/dbus/system_bus_socket
unix 3 [ ] DGRAM CONNECTED 236074
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 237931Networking To stop network and filter network connections, we use a
firewall. One such tool is iptables.
iptables
ewong25@lug-boat:~$ sudo iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destinationThese are the current firewall rules on the machine!
Closing Remarks
Thank you!
Closing Remarks
Capture the Flame 2025

Please join WiCyS for UIC’s first ever Capture the Flag event! A fun intercollegiate event tackling real cybersecurity challenges. You’ll be able to team up with friends or other schools, meet professionals, and compete for fun prizes.
Join the WiCyS Discord!
Closing Remarks
Officers
The information in this presentation will be made availableon our
website!
https://lug.cs.uic.edu
Join our Discord!
2025-02-21